
What are PP-R or
PP-RCT pipes?
PP-R
Definition: PP-R stands for “polypropylene random copolymer.” It comprises a copolymer of propylene and at least one comonomer, where propylene constitutes more than 50% of the composition.
Overview: PP-R emerged as a high-temperature plastic pressure piping system initially utilized for plumbing and hydronic heating during the 1980s in Europe. Its introduction to North America occurred in the 2000s. Originally, PP-R found applications in various industrial sectors in Europe during the 1970s, with its inaugural industrial use in North America reported in 1986.
PP-R piping materials are obtainable in diverse wall types and thicknesses (e.g., SDR 7.4, SDR 9, SDR 11, SDR 13.5, etc.), tailored to requisite pressure ratings. Thicker-walled pipes exhibit higher pressure ratings, while thinner-walled variants present lower pressure ratings.
PP-RCT
Definition: PP-RCT stands for “polypropylene random copolymer with modified crystallinity and temperature resistance.” It constitutes a copolymer of propylene and at least one comonomer, with propylene constituting over 50% of the composition.
Overview: PP-RCT emerged as a high-temperature plastic pressure piping system initially employed for plumbing and hydronic heating in Europe and North America during the 2000s.
PP-RCT represents a newer generation of PP-R material, distinguished by superior long-term strength at elevated temperatures compared to earlier resins. PP-RCT materials boast approximately 25% higher stress capability and a 25% higher pressure rating than PP-R pipes of the same wall thickness at equivalent operating temperatures.
Commercially available PP-RCT resins may exhibit either alpha-phase crystallinity or a blend of alpha and beta phase crystallinity, facilitated by a beta nucleating agent.
PP-RCT piping materials are offered in diverse wall types and thicknesses (e.g., SDR 7.4, SDR 9, SDR 11, SDR 13.5, etc.), tailored to requisite pressure ratings. Thicker-walled pipes offer higher pressure ratings, while thinner-walled counterparts present lower pressure ratings.
The history of PP-R and PP-RCT pipes
The development of polypropylene (PP) pipes began in the 1970s in Europe for industrial applications, particularly in the chemical and food industries. In the 1980s, PP pipes found their way into sanitary and heating installations due to their excellent resistance to chemicals and high temperatures. Since the 2000s, they have also become widespread in North America. As a further development, PP-RCT pipes were introduced to offer improved performance properties such as higher long-term strength at elevated temperatures.
International standards and certifications of PP-R & PP-RCT pipes
PP-R and PP-RCT pipes comply with rigorous international standards and certifications, including ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (German Institute for Standardization), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), and NSF (National Sanitation Foundation). These standards ensure the highest quality and safety for use in sanitary and heating applications.
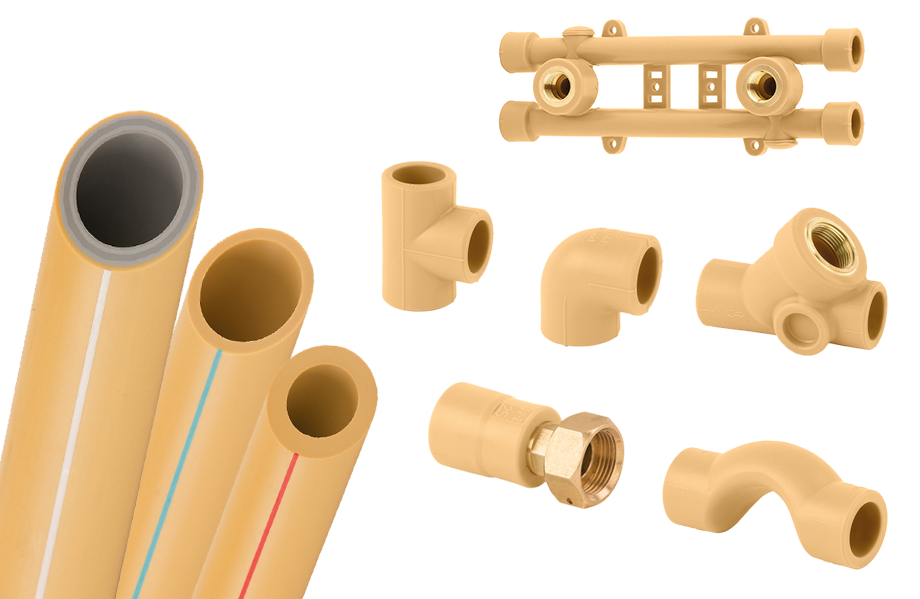
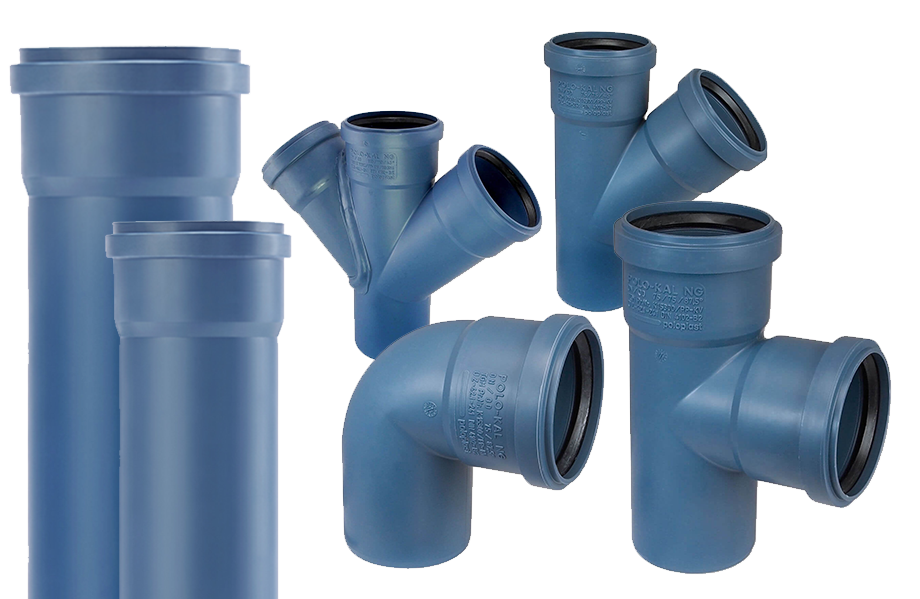
Various wall thicknesses and sizes of PP-R & PP-RCT pipes
PP-R and PP-RCT pipes are available in a variety of wall thicknesses, characterized by the Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR). This allows for adaptation to different pressure requirements and applications. Sizes range from small diameters for residential installations to large diameters for industrial applications such as chemical processing and cooling systems.
Connection and welding of PP-R & PP-RCT pipes
PP-R and PP-RCT pipes are connected using heat fusion, a reliable method where the pipe ends are heated and then fused together to create a solid connection. This method ensures leak-free installation and long-term durability of the piping systems.
Advantages of PP-R & PP-RCT pipes
- Potable water safety (certified to NSF/ANSI/CAN 61) and long-term reliability (certified to NSF/ANSI 14*)
- Resistance to corrosion, tuberculation, and deposits
- Resistance to chlorine and chloramine disinfectants
- Typically reduced product and installation costs compared to metallic piping systems
- Heat-fused joints obviate the need for flame, glue, or solvents for joining
- Lightweight, facilitating off-site fabrication, transportation, and on-site handling
- Natural insulating properties with low thermal conductivity
- Durability and toughness conducive to withstanding jobsite installations
- No scrap value, minimizing susceptibility to jobsite theft
- Available in a wide range of sizes Imparts a professionally installed appearance
- Piping products are typically certified to NSF/ANSI 14 for physical, performance, and health effects requirements
- Environmental Friendliness: PP-R and PP-RCT pipes are recyclable and have a low environmental impact, making them a sustainable solution for your projects.
Applications of PP-R & PP-RCT pipes
- Distribution of hot and cold water in residential and commercial areas
- Collection and distribution of treated water
- Hydraulic distribution for radiators, convectors, fans
- Use for hydraulic applications
- Use for heating, cooling, air conditioning
- Cooling water and condensate water for cooling towers, data centers, and supercomputers
- Industrial pipelines and process pipelines
- Compressed air
- And many more.
POLYMELT product solutions
ECOSAN
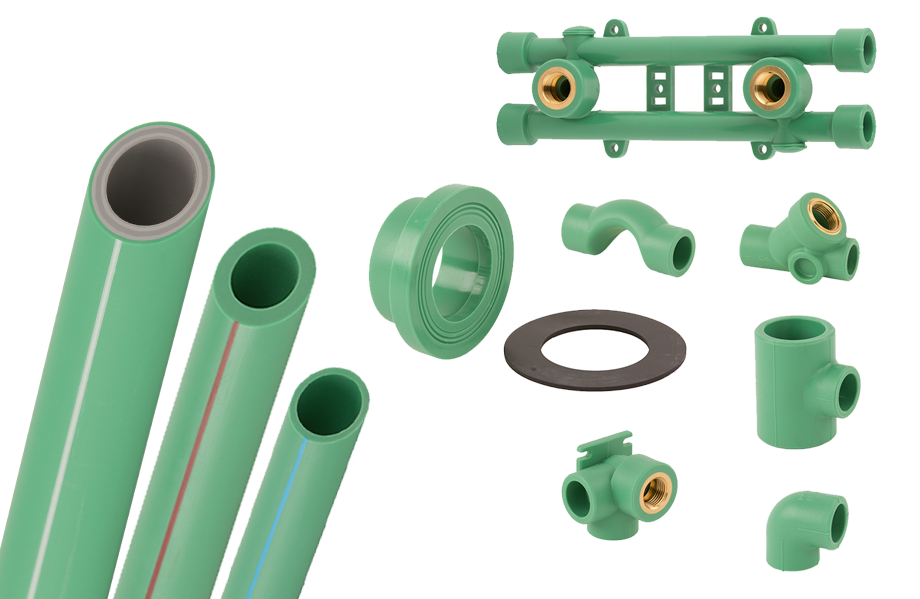

POLYMUTAN
UV
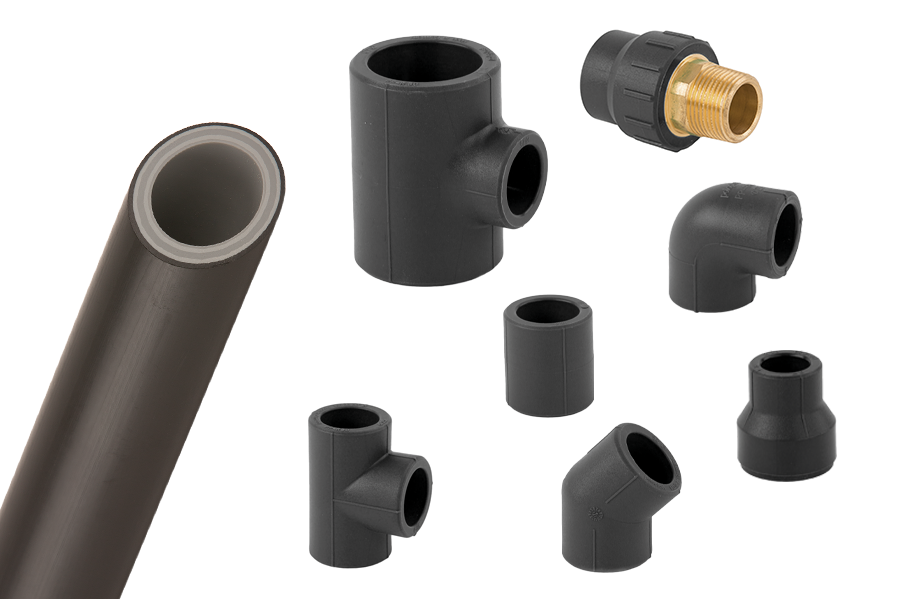

MECHANICAL
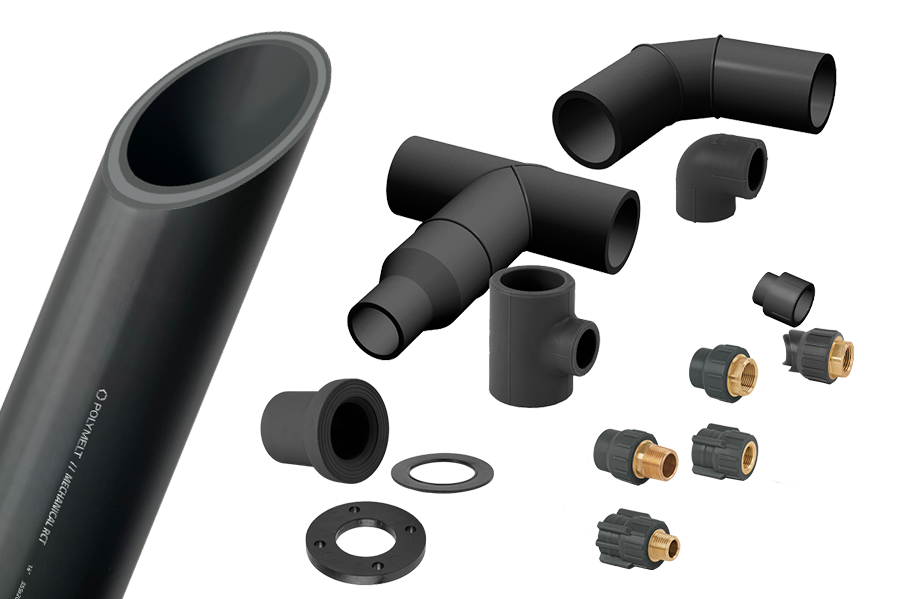

KAL-NG


Need more information?
Please contact us.
